Volunteering Program
Agricultural & Wildlife
Basic Farm Work
Here you will learn the day to day running of the farm.
- Development projects: rehabilitation camps, building water sources for new camps and other needed structures, accommodations etc.
- Visual patrols on foot: looking for objects that can injure the wildlife, like looking for wires, tracks, etc.
- Rehabilitation of old farmland: breaking down of old fences, disposing of rubbish, wires and snares, vegetation control, setting up needed developments,
- Field assessment: field assessment is highly crucial on how many species can be kept on the land, what type of management plan is required. Vegetation assessment will be needed on regular bases to assess the farms carrying capacity.
- Dam and water management
- Rain gauges: Good record keeping and management of the amount of rain that has fallen.
- Firebreaks: Help maintain firebreaks.
- Farm maintenance: Leaking water troughs, setting new pipelines for new water sources, dam management, and solar panel maintenance.
- Fence maintenance: Fences need to be patrolled and fixed where broken by animals
- Gardening: Help set up & grow our garden around the tented camp & volunteer camp
Lucerne Field (ALFALFA)
We developed a 6ha Lucerne field which with an underground drip irrigation and powered with solar electricity. Our aim is to increase the size to 19ha in order to de able to feed all animals on the farm should there be a drought year.
- Basic: General maintenance, irrigation & cultivation of Lucerne field, ensuring the success of the Lucerne growth, sowing seeds, growth, harvesting and baling.
- Water structure: adequate for the Lucerne as well as problems with pipes, sprinkler systems need rotation etc.
- Pest control: Rodent, termite and other pest control and putting up owl boxes
Vegetable & Fruit Garden
- Basic Gardening, Vegetables (Annual Plants, Perennial Plants, Shrubs) Fruit Trees, Nut Trees, Water Plants, Germination, Propagation, Grafting, Tree Management, and Fungi
- Water Resources, Water Collection/Storage, Irrigation and Grey Water Processing
- Building,Walling, Fencing, Dams/Ponds, Swales/Berms and Raised Beds
- Waste Management systems, Composting Toilets, Composting, and Worm Farms
Wildlife
- Beehives & owl boxes help build and put up
- Construct a (little) pond, Birds, lizards, spiders, dragonflies, chameleon, frogs will be attracted. They eat insects, which harm the crops. Create a system for them. Provide a habitat by making little houses for them.
- Construct birdhouses. Water features.
- Day to day cleaning: Cleaning of water sources and feeding bowls, cleaning of tack, cleaning of camps. Hygiene where food is prepared.
- Basic care & Fieldwork: Identification of animal, condition determination, health, wounds, any abnormalities, pregnancy, calving, record keeping, reacting to problems, etc.
- Feeding: In the dry season, the wildlife will be fed. This is a great time to get information on the individual animal. Assist in preparation of the food for the different animals, feeding, and monitoring (as mentioned in basic care & Farm work).
- Assist in training of animals: Getting individual animals into specific areas for capture if wounded or for other management purposes. Getting feeding areas up and running: development of fences and cable, possible electric wire, clear rocks, and possible bush clearing. Ensure gates work correctly.
- Camp management: Field assessment on the vegetation diversity and palatability so that the camps are stocked adequately.
- Necessary maintenance: Check water troughs and pipelines for leaks and any problems as well as fences.
- Administration: Record keeping of all animals,
- Game capture: Help with game capture
- Injured animals: Help treat and look after the sick and wounded animals
- Administration: Help with day to day administration
- Clinic: Cleaning of the clinic, equipment & helping out where needed.
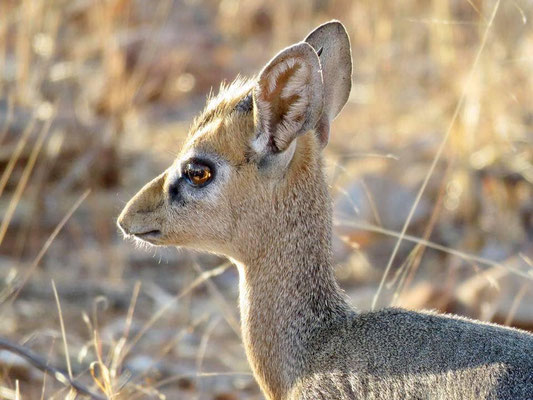
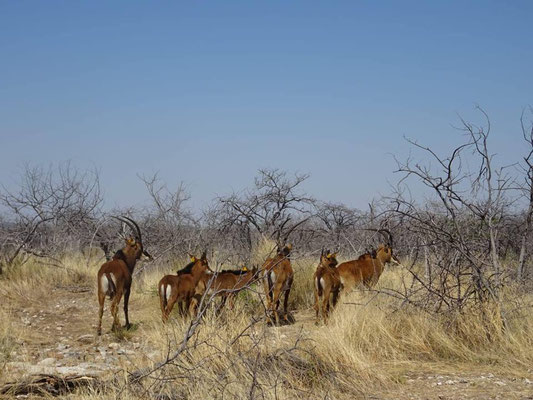
- Game Count: Herbivores of all sizes are an integral part of African ecosystems. It is creatural to understand local ungulate population dynamics and migrations to ensure enough water supply. At the same time, ungulate populations need to be assessed against the available vegetation to avoid damage to the ecosystem, for example from overgrazing. The volunteers will participate in regular game counts on either horseback, in the hide at the waterhole or by car to assist these monitoring efforts. Muller Stud is home to large herds of Oryx (gemsbok), Kudu, Eland, Sable, Water Buck, Springbuck and many more, but also contains fewer known species such as the Dik-Dik, Klipspringer etc. Ostrich populations will also be counted.
- Camera traps: Downloading and viewing of photos, making notes, and placing them incorrect files. This resource is also vital to the reserve and helps with identification as well as continuous monitoring of wildlife populations we also rely on motion-triggered camera traps. Because the cameras record data 24/7 and every day of the year, they often capture information that humans might have missed. The cameras are non-selective and therefore capture data on all wildlife that pass in front of them, be they carnivores, herbivores, birds or others. This helps the researchers assess which species are present, and where they are most active, especially for animals that are usually very cryptic or entirely nocturnal such as the Hyena’s, Cheetahs and even the Bush babies. The cameras are non-invasive and sometimes record interesting behavioural data that we would otherwise have no access to. Volunteers will help set cameras in the field (for example at water points, cheetah marking trees, caves etc.), maintain them (refresh batteries and memory cards) but also go through the abundance of images to assess and structure the data recorded.

Research & Data Basing
Veterinary / Wildlife Management / Ornithology / Wildlife Biology / Conservation / Forestry / Zoology
We would like all students to be involved in building our database on various species & submitting data to Virtual Museum @ ADU (Animal Demography Unit, http://vmus.adu.org.za)
Please create an account with the ADU and get familiar with the website & also download the BirdLasser App (for birds) & get familiar with the APP.
- Birds http://sabap2.adu.org.za/ BirdLasser App(free)
- Mammals
- Dung Beetles
- Trees
- Vegetation & Grass
- Snakes & other Reptiles
- Frogs
- Insects
- Mushrooms
- Any other interesting species found